IP Camera Basic Features
IP (Internet Protocol) cameras, also known as network cameras, are digital video cameras that transmit video and audio data over an IP network, such as a local area network (LAN) or the internet.
IP Camera key Features
- Digital Video Capture: IP cameras capture video in a digital format, allowing for high-quality video recordings. They use image sensors, such as CMOS or CCD, to capture video frames. The resolution and image quality of an IP camera can vary, ranging from standard definition (SD) to high definition (HD) or even ultra-high definition (UHD) resolutions.
- Network Connectivity: IP cameras are equipped with network interfaces, typically Ethernet ports, to connect to a network infrastructure. They use protocols like TCP/IP to transmit video and audio data over the network. This connectivity allows for remote access, configuration, and monitoring of the camera from anywhere with network connectivity.
- Power Options: IP cameras can be powered through various methods. Some cameras are powered by an external power supply connected to an electrical outlet, while others support Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology. PoE cameras receive power and data through a single Ethernet cable, simplifying installation and reducing cable clutter.
- Video Compression: To efficiently transmit video data over the network, IP cameras use video compression algorithms. Common video compression formats include H.264, H.265 (also known as HEVC), and newer codecs like AV1. Compression reduces the file size of the video without significantly compromising the quality, ensuring smooth transmission and efficient storage.
- Power Options: IP cameras can be powered through various methods. Some cameras are powered by an external power supply connected to an electrical outlet, while others support Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology. PoE cameras receive power and data through a single Ethernet cable, simplifying installation and reducing cable clutter.
- Image Adjustments: IP cameras often include features for adjusting the camera’s image parameters. These settings allow users to customize aspects such as brightness, contrast, saturation, sharpness, and white balance to optimize the image quality based on the environment and lighting conditions.
- Remote Access and Management: IP cameras offer remote access capabilities, allowing users to view live video feeds, playback recorded footage, and manage camera settings from a web browser, dedicated software, or mobile apps. This remote accessibility is valuable for real-time monitoring, reviewing recordings, and configuring camera settings remotely.
- Integration and Analytics: IP cameras can integrate with various systems and software applications for advanced functionalities. They can connect with video management systems (VMS) for centralized management and recording, access control systems for enhanced security, and analytics software for features like motion detection, facial recognition, or object tracking.
- Storage Options: IP cameras offer different storage options for video recordings. They may have built-in storage, such as onboard SD cards or solid-state drives (SSD), or support network-attached storage (NAS) devices or cloud storage services for centralized and scalable storage solutions.
- IP cameras provide flexible and scalable surveillance solutions, suitable for a wide range of applications, including home security, business surveillance, public safety, and more. Their digital nature, network connectivity, and advanced features make them highly capable and adaptable devices for capturing and managing video data.
IP Camera Structure
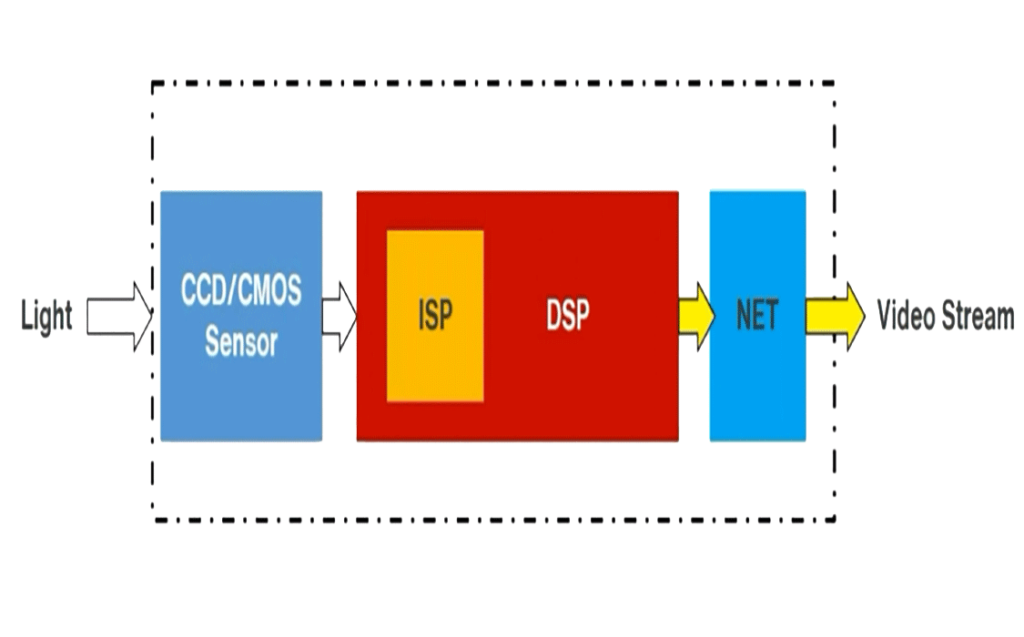
An IP camera is composed of lens, sensor(CCD/CMOS), ISP, DSP and related circuits.
Key Features Of CCD SENSOR
CCD stands for Charge-Coupled Device. It is a type of semiconductor sensor that is used to capture images. CCDs are used in a wide variety of devices, including digital cameras, scanners, and telescopes.
CCDs work by converting light into electrical signals. When light hits a CCD, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material. These electrons are then transferred to a series of capacitors, where they are stored. The amount of charge in each capacitor is proportional to the amount of light that hit it.
The electrical signals from the capacitors are then amplified and converted into a digital signal. This digital signal is then stored in the camera’s memory or sent to a computer for further processing.
CCDs have a number of advantages over other types of sensors, such as film. CCDs are more sensitive to light, which allows them to capture images in lower light conditions. They are also more stable than film, which means that they are less likely to be damaged by heat or humidity.
CCDs are also more efficient than film. They require less power to operate and they produce less waste.
As a result of these advantages, CCDs have become the standard sensor for digital cameras. They are also used in a variety of other devices, such as scanners, telescopes, and medical imaging equipment.
Here are some of the benefits of using CCDs:
- High sensitivity to light: CCDs are more sensitive to light than film, which allows them to capture images in lower light conditions.
- High image quality: CCDs can produce high-quality images with a wide range of dynamic range and color fidelity.
- Low noise: CCDs produce low-noise images, which is important for scientific and medical imaging applications.
- Durability: CCDs are durable and can withstand harsh environments.
- Cost-effectiveness: CCDs are cost-effective, which makes them a good choice for a variety of applications.
![]() However, it’s worth mentioning that in recent years, CCD sensors have been largely replaced by CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors in many consumer-grade and professional IP cameras. CMOS sensors offer advantages such as lower power consumption, faster readout speeds, and better integration with other camera functionalities.
However, it’s worth mentioning that in recent years, CCD sensors have been largely replaced by CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors in many consumer-grade and professional IP cameras. CMOS sensors offer advantages such as lower power consumption, faster readout speeds, and better integration with other camera functionalities.
Key Features Of CMOS SENSOR
CMOS sensors are the most common type of image sensor used in digital cameras. They offer a number of advantages over other types of sensors, such as CCD sensors.
Here are some of the key features of CMOS sensors:
- High speed: CMOS sensors can read out data much faster than CCD sensors. This makes them ideal for applications that require high frame rates, such as video recording and high-speed photography.
- Low power consumption: CMOS sensors consume less power than CCD sensors. This makes them ideal for battery-powered devices, such as smartphones and tablets.
- Larger pixels: CMOS sensors can have larger pixels than CCD sensors. This allows them to capture more light, which can improve image quality in low-light conditions.
- Lower noise: CMOS sensors produce lower noise than CCD sensors. This is due to the way that CMOS sensors read out data. CCD sensors read out data row by row, which can introduce noise. CMOS sensors read out data pixel by pixel, which reduces noise.
- Wider dynamic range: CMOS sensors have a wider dynamic range than CCD sensors. This means that they can capture a wider range of brightness levels in a single image. This can be useful for applications such as HDR photography.
CMOS sensors are becoming increasingly popular as the technology continues to improve. They offer a number of advantages over other types of sensors, making them a good choice for a variety of applications.
Here are some of the disadvantages of CMOS sensors:
- Less sensitive to light: CMOS sensors are less sensitive to light than CCD sensors. This means that they need more light to produce a good image.
- More prone to blooming: CMOS sensors are more prone to blooming than CCD sensors. Blooming occurs when a pixel is overexposed and spills its charge into neighboring pixels. This can cause a white spot to appear in the image.
- More expensive: CMOS sensors are more expensive than CCD sensors. This is due to the fact that they are more complex to manufacture.
Overall, CMOS sensors offer a number of advantages over CCD sensors. They are faster, more power-efficient, and have larger pixels. They also produce lower noise and have a wider dynamic range. However, they are less sensitive to light and more prone to blooming.
Key Features Of DSP
- DSP stands for Digital Signal Processor.
- In the context of an IP camera, it refers to a specialized chip or component that processes the digital signals received from the camera’s image sensor.
- The DSP in an IP camera performs several important functions to enhance and optimize the captured video stream.
Some key roles of the DSP in an IP camera:
- Image Processing: The DSP processes the raw digital data from the image sensor and applies various algorithms and filters to improve the quality of the image. This may include functions such as noise reduction, sharpness enhancement, color correction, and dynamic range adjustment. The DSP helps to optimize the captured image for better visibility and clarity.
- Compression: IP cameras typically capture high-resolution video, which can generate large amounts of data. The DSP plays a crucial role in compressing the video stream using codecs like H.264 or H.265. Compression reduces the size of the video file without significant loss of quality, allowing for efficient storage and transmission over network connections.
- Video Analytics: Many IP cameras offer advanced video analytics features, such as motion detection, object tracking, facial recognition, and people counting. The DSP processes the video stream to analyze and interpret the visual data, enabling these intelligent functionalities. This allows the camera to detect specific events or objects and trigger appropriate actions or notifications.
- Network Protocol Support: The DSP handles the encoding and decoding of the video stream to conform to various network protocols used in IP camera systems, such as TCP/IP, HTTP, RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol), and ONVIF (Open Network Video Interface Forum) standards. It ensures compatibility and seamless integration with other devices and video management systems.
- Adjustments and Control: The DSP provides controls for adjusting camera settings, such as exposure, white balance, and focus. These controls can be remotely accessed and adjusted through the camera’s user interface or management software, allowing for flexible and convenient configuration. applications.
![]()
Overall, the DSP in an IP camera plays a crucial role in optimizing the captured video stream for better image quality, efficient storage, intelligent analytics, and seamless network integration. It enables the IP camera to deliver high-performance video surveillance capabilities suitable for various applications.
ISP In IP Camera
Key Features Of ISP
- ISP stands for Image Signal Processor.
- In the context of an IP camera, it refers to a dedicated hardware component or chip that processes the raw image data from the camera’s image sensor before it is further processed or transmitted.
- The ISP in an IP camera performs several important functions to enhance and optimize the image quality.
key roles of the ISP in an IP camera
- Demosaicing:
- In many digital cameras, including IP cameras, the image sensor uses a color filter array (commonly known as a Bayer filter) to capture color information.
- The ISP performs demosaicing, which involves interpolating the missing color information and reconstructing the full-color image from the sensor’s raw data.
- Noise Reduction:
- The ISP applies various noise reduction techniques to minimize unwanted noise and artifacts present in the captured image.
- It analyzes the image data and selectively reduces noise while preserving image details to improve image quality, especially in low-light conditions.
- Color Correction and White Balance:
- The ISP adjusts the color balance of the image to ensure accurate reproduction of colors.
- It performs color correction and white balance calibration to eliminate color casts caused by different lighting conditions and to maintain color fidelity.
- Gamma Correction and Tone Mapping:
- The ISP adjusts the image’s gamma curve to optimize the brightness and contrast levels.
- It applies gamma correction and tone mapping algorithms to enhance the overall tonal range of the image, resulting in improved dynamic range and better visibility of details.
- Sharpness Enhancement:
- The ISP enhances the sharpness of the image by applying edge enhancement algorithms.
- It detects edges and increases their contrast, resulting in a sharper and more defined image.
- Exposure Control:
- The ISP controls the camera’s exposure settings, including shutter speed, aperture, and gain, to ensure proper exposure of the image.
- It analyzes the image data and adjusts these parameters dynamically to handle different lighting conditions and prevent overexposed or underexposed areas.
- Lens Distortion Correction:
- The ISP corrects any optical distortions introduced by the camera lens.
- It applies geometric transformations to rectify barrel distortion or pincushion distortion, resulting in more accurate and distortion-free images.
![]()
The ISP plays a critical role in optimizing the image quality before it is further processed, compressed, or transmitted by the IP camera. It ensures that the captured images are of high quality, accurately represent the scene, and provide useful visual information for surveillance or other applications.
Related Circuits
- Analog Front-End (AFE): The AFE circuitry is responsible for processing the analog signals from the image sensor. It typically includes components such as amplifiers, analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), and programmable gain stages. The AFE circuit amplifies and conditions the weak analog signals from the image sensor before they are converted into digital signals for further processing.
- Timing and Control Circuits: These circuits generate and synchronize the timing signals required for proper operation of the image sensor and related components. They control the readout, exposure time, and other parameters of the image sensor. Timing and control circuits ensure the accurate capture and transfer of image data.
- Digital Processing Unit (DPU): The DPU is responsible for handling the digital processing tasks, such as image processing, compression, and encoding. It typically includes a digital signal processor (DSP) or a dedicated image processing chip. The DPU performs tasks like noise reduction, color correction, compression, and video encoding to optimize the captured image data for storage or transmission.
- Memory Interface: The memory interface circuit allows the camera system to store and retrieve image data from memory devices, such as RAM (Random Access Memory) or flash memory. It handles the data transfer between the DPU and the memory, ensuring efficient storage and retrieval of image data.
- Power Management Circuit: The power management circuit regulates and distributes power to the various components of the camera system. It includes voltage regulators, power monitoring circuits, and battery management systems (in battery-powered devices). The power management circuit ensures stable and efficient power supply to the camera components for reliable operation.
- Communication Interface: Cameras often have communication interfaces to transfer image data or control signals to external devices. This may include interfaces such as USB (Universal Serial Bus), Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or other proprietary protocols. The communication interface circuit handles the encoding, decoding, and transfer of data between the camera and other devices.
![]() These are just a few examples of related circuits that are integral to the functioning of camera systems. The combination and complexity of these circuits may vary depending on the camera type, application, and desired features. Each circuit serves a specific purpose in capturing, processing, and transferring image data to ensure optimal performance and image quality.
These are just a few examples of related circuits that are integral to the functioning of camera systems. The combination and complexity of these circuits may vary depending on the camera type, application, and desired features. Each circuit serves a specific purpose in capturing, processing, and transferring image data to ensure optimal performance and image quality.
Different Product Families Of Hikvision IP Cameras
Value Series
- 1 Series
- Wi-Fi Series
Pro Series
- Easy IP 1.0 Plus
- Easy IP 2.0 Plus
- Easy IP 3.0
- Easy IP 4.0
Ultra Series
- 3 Series
- 5 Series
Special Series
- Covert Series
- Standalone Security Site
Deepen View Series
- 7 Series
- 8 Series
Key Features Of Ultra Series (SmartIP)

24/7 Coverage with details and color
Abundant and numerous choices for a variety of needs

AI-automated security protection
Many camera models of the Ultra Series are embedded with a deep-learning algorithm to distinguish persons and vehicles from other moving objects. Select models are able to automatically ward off detected trespassers with visual and auditory warnings.